| Long Reach Ethernet | |
|
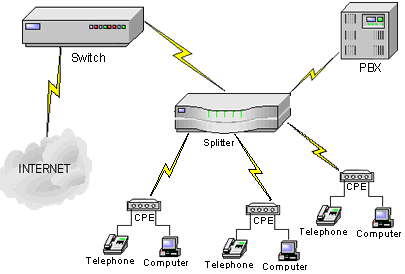
The endless demand of delivering greater amount of data over longer distances will continually increase as new information technologies continue developing. To meet this demand researchers are working on technologies that will enable simultaneous voice and data transfer applications. The technologies that have been available up until now usually required obtaining a separate hardware device, as in the ISDN and xDSL technologies, to transfer voice along with data simultaneously; moreover this application was not favorable in local area networks (LANs). A group of researchers tried to find answers to the question of delivering a mix of data that travels over a local network and voice on the same medium without requiring any rewiring of the infrastructure. As a result of these efforts and the leading role of Cisco, "Long Reach Ethernet (LRE)" technology, which enables the transportation of data that travels across a local network and voice together, on any of two wires over long distances, was achieved. The current local area standards enable data transportation over 4 wires. In today's new cabling applications, a cable with 8 wires is used and this is called CAT-5 cabling. This cable transports local area data at a distance of maximum 100 meters. However, there are some shortcomings of this widely used standard as for the designers of network infrastructures. Disadvantages of this standard such as the distance over which you will transport the local area network data is limited to 100 meters, or a totally new cabling application is necessary since it uses 4 wires etc. LRE comes up as a technology that overcomes the shortcomings and that creates the suitable environment to simultaneously transport analog telephone calls, data similar to ISDN, DSL and data traveling over a local area network. Any of the 2 wires are used with Long Reach Ethernet contrary to the typical standard application. By simply using the existing telephone wire infrastructure in the buildings, it is possible to bring local area network connection to the computers of all the users -without any interference to their telephone calls- from the same connection. Three hardware devices are needed to install LRE system. The first one is a device that includes two standard RJ-11 telephones at the side of the user end and a RJ-45 ethernet port. One of the telephone sockets will be connected to the telephone of the user, the other socket will be connected to the telephone wire in the wall if the current telephone infrastructure is going to be used and RJ-45 socket will be connected to the ethernet card of the user's computer. This device delivers two groups of data below and under 700 kHz. The information below 700 kHz is used by analog phone calls, ISDN, DSL and similar technologies. The information is transported, without undergoing any changes, to the telephone connection (or to any of the 2 wires that are used). If the information is local area network data, the device modulates the data used in the local network above 700 kHz and transmits it to the receiver by using the telephone line in the wall (or any of the two wires). This process enables the transportation of both voice and local network data simultaneously over a long distance by simply using 2 wires similar to that of telephone wires. The second device is a splitter that separates the voice and data that comes from the users. It transmits the local network data to the switch, and it directs the voice and the signals under 700 kHz to the PBX system. Since there is no software that runs on the splitter, it does not need any configuration or console port. The third and last device is a switch that will process the local network data received from the splitter. Some of the ports of the switch contain a standard RJ-45 connector to connect other servers and switches to the device, whereas the ports where the local network data enters contain 2 wires. The device could provide a bandwidth up to 15 Mbps to each of its ports without sharing. In this bandwidth, LRE can also transmit POTS, DSL and ISDN signals to the receiver in addition to its own local network data. The general structure of the whole system is given in Figure-1.
The bandwidth decreases in regard to the distance when the local network data travels over two wires. When we think of the typical UTP data lines, which are limited to 100 meters at 10/100 Mbps bandwidth, LRE technology changes these limits as indicated on Table-1. |
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Delivery of data and voice over one line will be cost effective since it prevents rewiring. If, in the future, the limits of distance and speed could be increased, the engineers that design networks in new cable structures will have to consider this LRE technology as well. | ||||||||||||
| - TOP - | ||||||||||||
Design: CC - INFO